Local Anaesthesia Reversal and Gums and New born connection
Local Anaesthesia Reversal 10 May
Drooling, biting your lip and talking like you have marbles in your mouth after a visit to the dentist could soon become a thing of the past.
A drug that reverses the numbing effects of local anesthesia used by dentists was approved yesterday by the Food and Drug Administration for patients as young as 6 years old.
OraVerse, which was developed by private San Diego company Novalar, is the first dental anesthesia reversal agent on the market. It cuts in half the time it takes for Novocaine and other numbing agents to wear off, according to clinical studies.
That amounted to about 85 fewer minutes of numbness during clinical trials. About 40 percent of patients in the trials felt sensation return within an hour of receiving the OraVerse injection.
Full Report Here
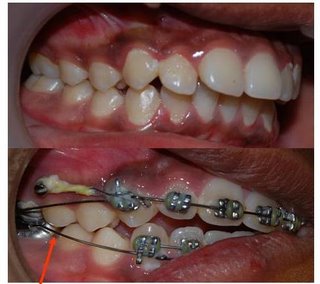
Molar Distalisation with Mini implants
This has been proved in number of studies that micro or mini implants in orthodontic patients can cut treatment time upto 40%. In the last post we had posted two studies from AJODO which show how quality of treatment would be better with MIA because of better anchorage management. What are you waiting for ? start using microimplants now, they are easy to use and inexpensive, learn more now.
Here we have posted a pic of molar distalisation done in less than six months, start date is 5 Nov 2007 and second pic is taken on 12 May 2008, if you see facial change you will be happy -to see all the intraoral and facial pictures CLICK HERE.
Periodontal disease and adverse birth outcomes: a study from Pakistan
American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology -Volume 198, Issue 5, May 2008
There have been several reports that gingival condition during pregnancy should be maintained well to avoid adverse outcomes. This study once again proves that point. Our goal should be to cater to the needs of each and every pregnant lady and Gynecologists should be educated to refer all such patients for routine maintenance and treatment.
Study Design
This was a prospective cohort study. Enrollment occurred at 20-26 weeks of gestation. A study dentist performed the periodontal examination to assess probing depth, clinical attachment level, gingival index, and plaque index. Outcomes included stillbirth, neonatal death, perinatal death, <32 style="font-weight: bold;">Results
Dental examinations and outcome data were completed for 1152 women: 81% of the women were multiparous, with a mean age of 27 years; 33% of the women had no education. Forty-seven percent of the women had dental caries; 27% of the women had missing teeth, and 91% of the women had had no dental care in the last year. Periodontal disease was common: 76% of the women had ≥3 teeth with a probing depth of ≥3 mm; 87% of the women had ≥4 teeth with a clinical attachment level of ≥3 mm; 56% of the women had ≥4 teeth with a plaque index of 3; and 60% of the women had ≥4 teeth with a gingival index of 3. As the measures of periodontal disease increased from the 1st to 4th quartile, stillbirth and neonatal and perinatal death also increased, with relative risks of approximately 1.3. Early preterm birth increased, but the results were not significant. Late preterm birth and low birthweight were not related to measures of periodontal disease.
Conclusion
Pregnant Pakistani women have high levels of moderate-to-severe dental disease. Stillbirth and neonatal and perinatal deaths increased with the severity of periodontal disease.
Drooling, biting your lip and talking like you have marbles in your mouth after a visit to the dentist could soon become a thing of the past.
A drug that reverses the numbing effects of local anesthesia used by dentists was approved yesterday by the Food and Drug Administration for patients as young as 6 years old.
OraVerse, which was developed by private San Diego company Novalar, is the first dental anesthesia reversal agent on the market. It cuts in half the time it takes for Novocaine and other numbing agents to wear off, according to clinical studies.
That amounted to about 85 fewer minutes of numbness during clinical trials. About 40 percent of patients in the trials felt sensation return within an hour of receiving the OraVerse injection.
Full Report Here
Molar Distalisation with Mini implants
This has been proved in number of studies that micro or mini implants in orthodontic patients can cut treatment time upto 40%. In the last post we had posted two studies from AJODO which show how quality of treatment would be better with MIA because of better anchorage management. What are you waiting for ? start using microimplants now, they are easy to use and inexpensive, learn more now.
Here we have posted a pic of molar distalisation done in less than six months, start date is 5 Nov 2007 and second pic is taken on 12 May 2008, if you see facial change you will be happy -to see all the intraoral and facial pictures CLICK HERE.
Periodontal disease and adverse birth outcomes: a study from Pakistan
American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology -Volume 198, Issue 5, May 2008
There have been several reports that gingival condition during pregnancy should be maintained well to avoid adverse outcomes. This study once again proves that point. Our goal should be to cater to the needs of each and every pregnant lady and Gynecologists should be educated to refer all such patients for routine maintenance and treatment.
Study Design
This was a prospective cohort study. Enrollment occurred at 20-26 weeks of gestation. A study dentist performed the periodontal examination to assess probing depth, clinical attachment level, gingival index, and plaque index. Outcomes included stillbirth, neonatal death, perinatal death, <32 style="font-weight: bold;">Results
Dental examinations and outcome data were completed for 1152 women: 81% of the women were multiparous, with a mean age of 27 years; 33% of the women had no education. Forty-seven percent of the women had dental caries; 27% of the women had missing teeth, and 91% of the women had had no dental care in the last year. Periodontal disease was common: 76% of the women had ≥3 teeth with a probing depth of ≥3 mm; 87% of the women had ≥4 teeth with a clinical attachment level of ≥3 mm; 56% of the women had ≥4 teeth with a plaque index of 3; and 60% of the women had ≥4 teeth with a gingival index of 3. As the measures of periodontal disease increased from the 1st to 4th quartile, stillbirth and neonatal and perinatal death also increased, with relative risks of approximately 1.3. Early preterm birth increased, but the results were not significant. Late preterm birth and low birthweight were not related to measures of periodontal disease.
Conclusion
Pregnant Pakistani women have high levels of moderate-to-severe dental disease. Stillbirth and neonatal and perinatal deaths increased with the severity of periodontal disease.

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home